Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -
- and high-resolution
and high-resolution  fine-structure spectroscopy for the heaviest nuclei
fine-structure spectroscopy for the heaviest nucleiAsai, Masato; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Nozomi; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Kaji, D.*; Morimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
no journal, ,
Alpha-gamma and high-resolution  fine-structure spectroscopy of Rf and Lr isotopes was performed to clarify the nuclear structure of superheavy nuclei.
fine-structure spectroscopy of Rf and Lr isotopes was performed to clarify the nuclear structure of superheavy nuclei.  rays following the
rays following the  decay of
decay of  Rf were observed for the first time through the
Rf were observed for the first time through the  -
- coincidence measurement, and the neutron configuration of the ground state of
coincidence measurement, and the neutron configuration of the ground state of  Rf was assigned. It was found that the ground-state configuration of
Rf was assigned. It was found that the ground-state configuration of  Rf is different from those of the lighter N = 155 isotones
Rf is different from those of the lighter N = 155 isotones  Fm and
Fm and 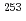 Cf. For the Lr isotopes, the proton configurations of the ground and isomeric states in
Cf. For the Lr isotopes, the proton configurations of the ground and isomeric states in  Lr and the ground states of
Lr and the ground states of  Lr and
Lr and  Lr were definitely identified through the high-resolution
Lr were definitely identified through the high-resolution  fine structure spectroscopy. Theoretical calculations based on the macroscopic-microscopic model revealed that the change of the ground-state configuration in the N = 155 isotones is strongly associated with the rapidly decreasing hexadecapole deformation with increasing atomic number.
fine structure spectroscopy. Theoretical calculations based on the macroscopic-microscopic model revealed that the change of the ground-state configuration in the N = 155 isotones is strongly associated with the rapidly decreasing hexadecapole deformation with increasing atomic number.
Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Aritomo, Yoshihiro; Comas, V. F.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Koura, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
Nucleus is a composite system consisting of protons and neutrons, and approximately 3000 nuclides have been identified experimentally. However, the existence of much more nuclides is postulated theoretically. How far the area of nuclei extends is an important question in nuclear physics. We have developed an original model based on the macroscopic and mean-field models to describe nuclear masses, called the KTUY (Koura-Tachibana-Uno-Yamada) mass model. By using the KTUY model, we have studied decay modes for alpha-decay, beta-decay, proton emission and spontaneous fission in the wide nuclear mass region. In the extremely heavier nuclear mass region, a large amount of nuclei located over 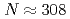 is predicted to exist. This region of nuclei with longer lives than 1ns ends or is disconnected at
is predicted to exist. This region of nuclei with longer lives than 1ns ends or is disconnected at 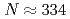 . The total number of nuclei having more than 1 ns is estimated to be ten thousands. If we focus on half-lives of 1 ms or longer, number of nuclei would be roughly eight thousands.
. The total number of nuclei having more than 1 ns is estimated to be ten thousands. If we focus on half-lives of 1 ms or longer, number of nuclei would be roughly eight thousands.
Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro; Li, Z.*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Sato, Tetsuya; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
no journal, ,
Electrochemical study of mendelevium (Md) with flow electrolytic column chromatography is presented. The  Md isotope was produced in the
Md isotope was produced in the  Cm(
Cm( B, 4
B, 4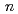 ) reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator. In applying a negative voltage on the column electrode, Md was eluted with 0.1 M HCl. This behavior is quite similar to that of Sr
) reaction at the JAEA tandem accelerator. In applying a negative voltage on the column electrode, Md was eluted with 0.1 M HCl. This behavior is quite similar to that of Sr and Eu
and Eu , clearly indicating that most stable Md
, clearly indicating that most stable Md is reduced to Md
is reduced to Md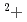 . We determined the redox potential of Md to be approximately -0.18 V versus a standard hydrogen electrode.
. We determined the redox potential of Md to be approximately -0.18 V versus a standard hydrogen electrode.
Sato, Nozomi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Li, Z.*; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sch del, M.; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
del, M.; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP) of the last actinide, lawrencium (Lr), is predicted to be lower than those of other actinides. To determine the IP of Lr based on the surface ionization comparison technique, we are developing a surface-ionization-type ion-source coupled to a gas-jet transport system at the Isotope Separator On-Line at the JAEA tandem accelerator facility. In the present study, we measured ionization efficiencies of lanthanides as a function of ion-source temperature to examine the applicability of our apparatus to the IP measurement. It was found that the obtained ionization efficiency of each lanthanide element is affected by an ionization potential as well as a boiling point.